Ligand Preparation
1. Overview of Ligand Preparation
The Ligand Preparation module is mainly used to help users clean small molecules. The module provides routine small molecule preparation methods, including removing unconnected groups (such as metal ions, salt ions), retaining the largest molecular fragments, generating isomers (ionic states, isomers, stereoisomers) and hydrogenation, and energy minimization. The panel settings for ligand preparation on our platform are as shown in Figure 2. The default selections on the page are the current optimal parameters, and users can also choose suitable parameters based on their knowledge. The parameters here are consistent with those in the "Ligand Preprocessing" module.
2. Instruction for Use
You can complete the calculation in just two steps: Determine the input method (default is to upload file) - Determine preprocessing parameters.
(1) Input Type
The platform provides two data input methods: upload file, and data center.
- Upload File
Check the "Upload File" box, and you can select a local file by clicking the button below. After the file is selected, the file name will be displayed on the button, and the file content will be displayed on the right. Regarding the uploaded files:
The currently supported file formats are .sdf and .csv. If an sdf file is uploaded, you can directly proceed to the next step. If a csv file is uploaded, you need to specify the smiles column.
The file size should not exceed 10MB.
- Data Center
Check the "Data Center" box, and a pop-up window will appear when you click the button below. Click on the file name to select data from the data center. After you click, the pop-up window will disappear and you can submit the task.
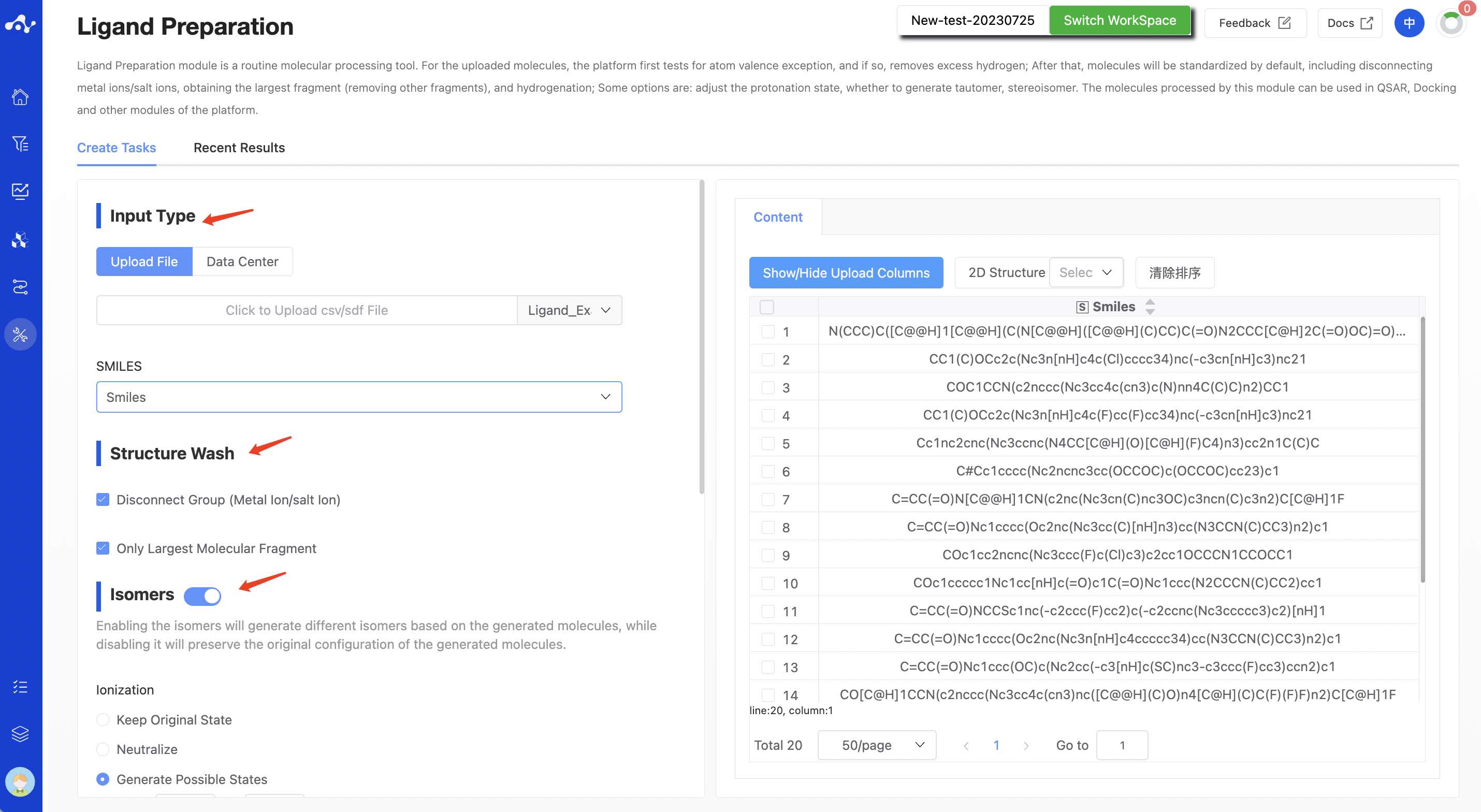
Figure 1. Input method - Upload file/Data Center
(2) Determine preprocessing parameters
- Structural cleaning
This step is mainly used to remove unconnected groups (including metal ions, salt ions) and retain the largest molecular fragments. By default, it is selected.
- Generate isomers
The current platform enumerates the uploaded molecules by default (the switch status is "on") in order to generate more isomers, including ionic isomers, tautomers, and stereoisomers. When the switch status is "off", the system will not do other processing on the molecules and will retain the original conformation of the molecules.
Ionic isomers. It generates possible ionization states by adjusting the pH value range;
Tautomers. It generates possible isomers based on the ionization state;
Stereoisomers. It generates possible isomers based on the chiral features of the molecule, or it can retain the original state.
Number of isomers. The platform defaults to output a maximum of 5 isomers. Users can adjust according to their needs.
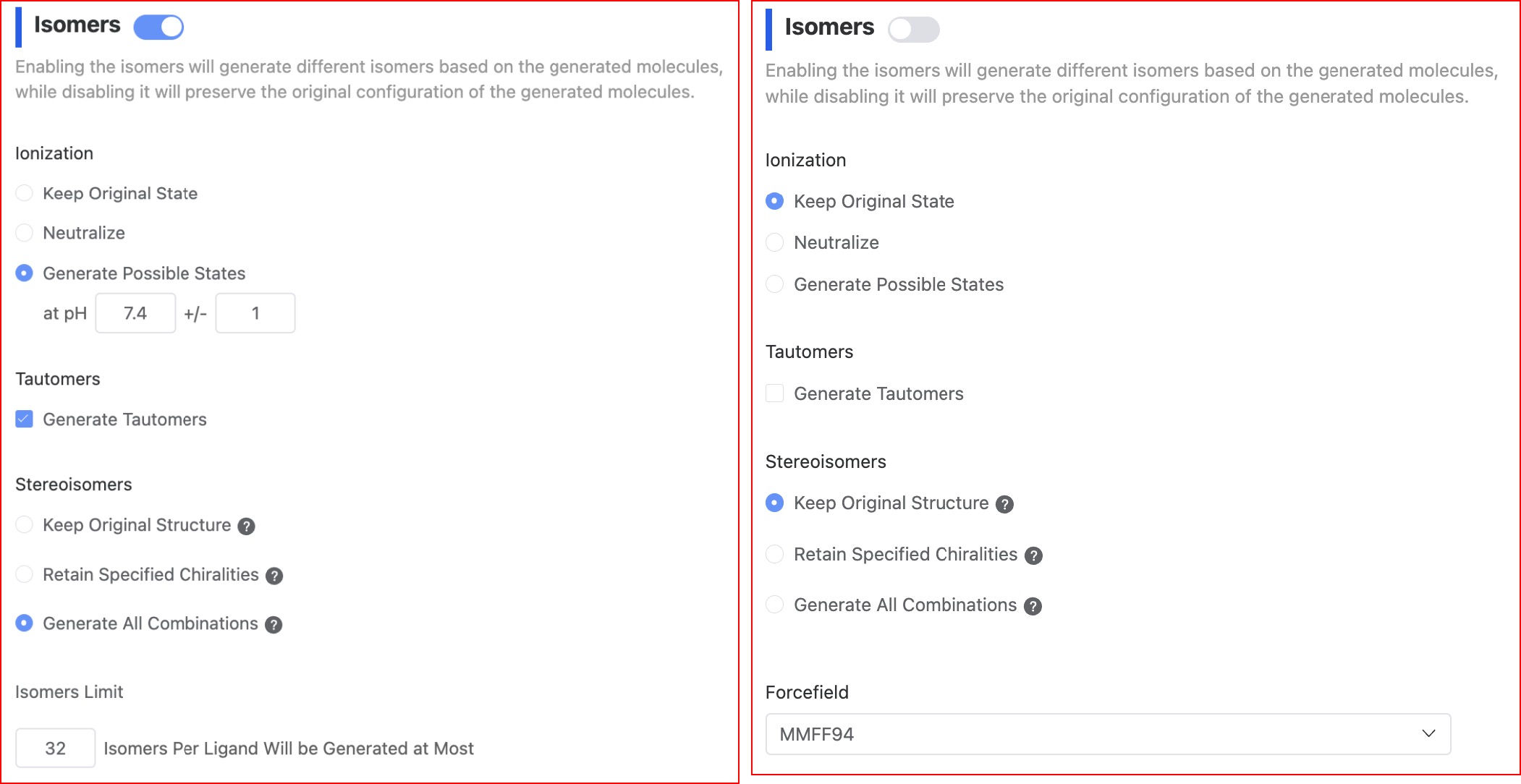
Figure 2. Isomer parameter settings
- Forcefield
MMFF94. MMFF is an abbreviation for Merck Molecular Force Field, a professional small molecule force field. It's the second-generation molecular force field developed by Hagler and is one of the most accurate force fields currently available.
UFF. UFF is an acronym for Universal Force Field. It is a general force field that covers the entire periodic table of elements. Its accuracy in calculating structures and binding energies is average, and it is used only when a suitable force field cannot be found.
(3) Running Sataus and View Results
After the task is submitted, the page will automatically jump to the "Recent Results" subpage of the current page. Here you can view the task running status of the current module (progress bar), and you can also view all running tasks of all modules in the "Running" dropdown box in the upper right corner. When the data volume is large, the system will calculate in batches, so as long as a batch of data is calculated (while the entire task is still running), you can click the "Result Details" button to enter the result page and view the prediction result list of the currently completed calculations (molecules that have not completed the calculation will not be displayed temporarily). You can also refresh the current page to get the latest completed data.
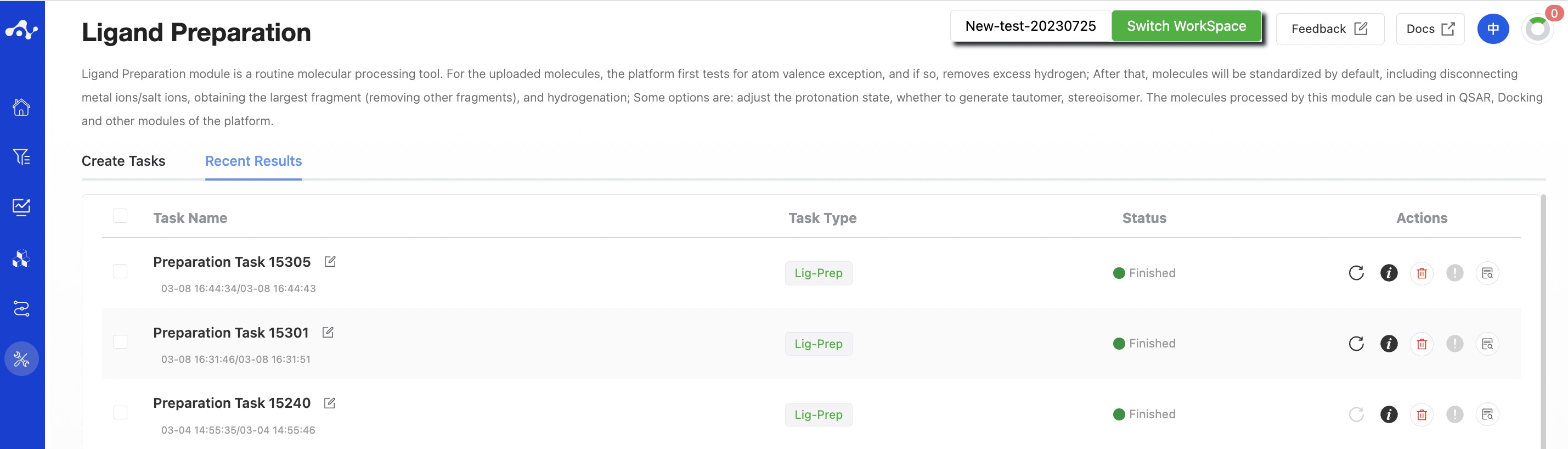
Figure 3. View Results
3. Results Analysis
The result page consists of the Summary at the top and the list in the middle. The result page is relatively simple, by default displaying two columns of data, namely ID and structure.
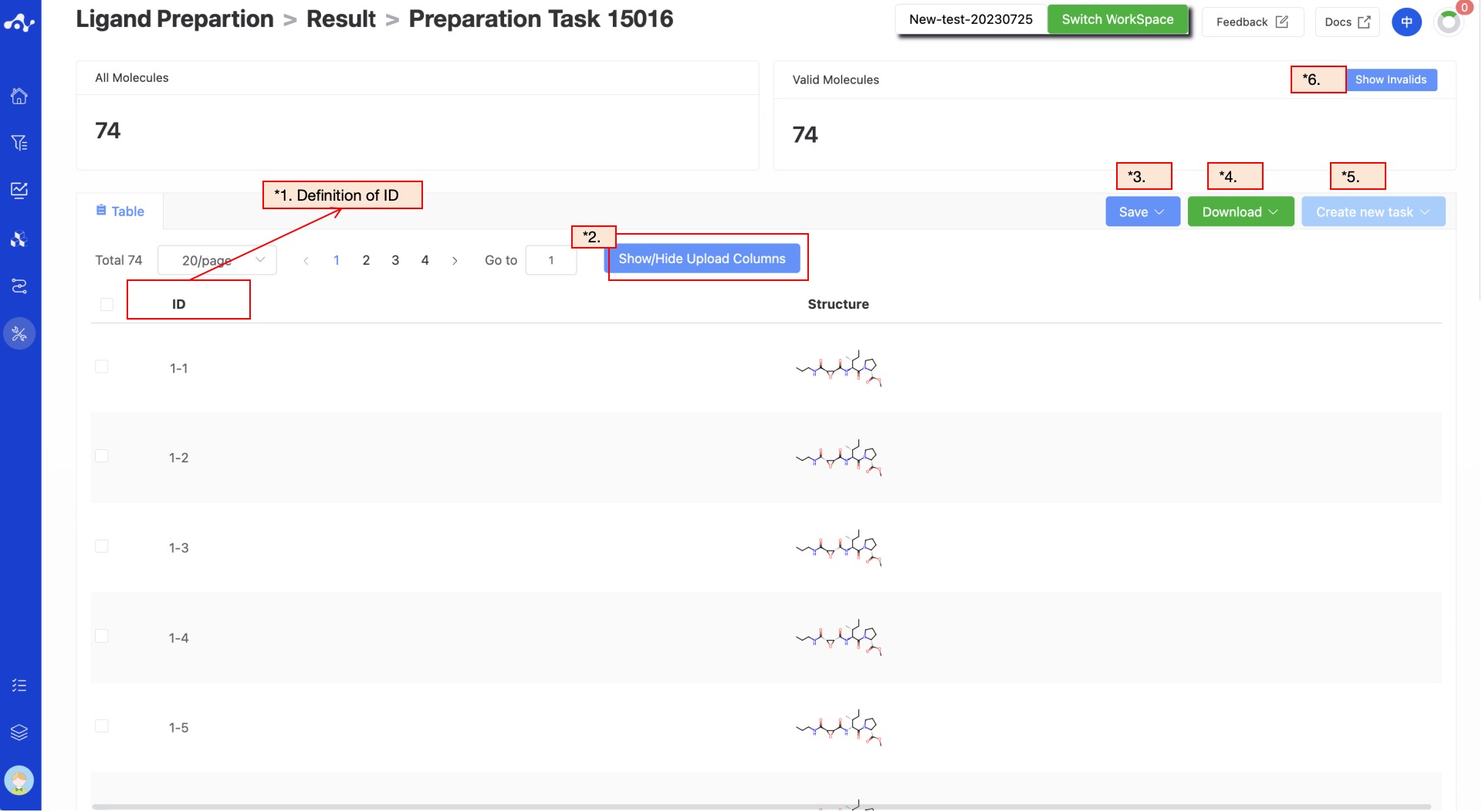
Figure 4. Results Page Function Distribution
(1) Meaning of ID in the table
The ID is assigned according to the molecule order in the original file. If the task does not generate isomers, the ID will be continuous values from 1 to N; if the task chooses to generate isomers, then the ID will be a combination of X-Y-Z. X represents the order of molecules, Y represents the number of isomers of the molecule, and Z represents the number of conformations output. The smaller the Y value, the higher the likelihood of this isomer existing.
(2) Show/Hide Upload Column
The default result list does not display information in the uploaded file, so it is unselected in the left control bar. When you don't want to display this property, deselect it, and the result list on the left will show in real time based on the selection in the control bar. At the top, there are also two shortcuts "Select All" and "Deselect", which are convenient for users to quickly select.
(3) Save
Click "Save", and the system will pop up a dropdown box for you to choose the file format to save (currently only supports .csv/.sdf). Once you have determined the style of the file to save, save the corresponding data to the data center as a sdf or csv file. The saved content is the molecules of the effective number displayed on the page, which are usually obtained according to your show/hide column conditions, advanced filtering conditions, favorites, or dislikes.
(4) Download
Click "Download", and the system will pop up a dropdown box for you to choose the file format to download (currently only supports .csv/.sdf). After determining the style of the file to download, the system will download the corresponding data to your local device as a sdf or csv file. The content downloaded is consistent with the save method, which also downloads the molecules of the effective number displayed on the page, which are usually obtained based on your show/hide column conditions, advanced filtering conditions, favorites, or dislikes.
(5) Create New Task
The prerequisite for creating a new task is to first save the data into a file. Before the save operation is performed, this button is disabled. As soon as the new file is saved based on the results, this button is enabled. When you click this button, the system will pop up a dropdown box for you to select the module to be calculated. After clicking, the page will immediately open a new tab and will take your saved dataset with it. After adjusting the parameters, you can submit a new task.
(6) Hide Invalid Molecules
For SMILES errors or molecules that cannot be resolved in the back-end, the algorithm cannot perform the correct calculation, in which case the task is unaffected, but the molecule is defined as invalid. Users can use the "Hide invalid molecules" button to quickly filter out the part of the molecule.
