Inno-PepDocking
1. Inno-PepDocking Overview
Inno-PepDocking is a peptide docking module based on RAPiDock, which is a protein-peptide docking method based on diffusion generative models. It enables fast, accurate, and reasonable molecular docking at the all-atom level. It achieves a 93.7% Top-25 prediction success rate on the RefPepDB-RecentSet test set, representing a 13.4% improvement over AlphaFold2-Multimer, with approximately 270 times faster prediction speed (about 0.35 seconds per complex). It supports all-atom modeling for 92 types of amino acid residues, including various post-translational modifications.
2. Usage Instructions
(1) Protein Preprocessing
Input Protein
- Upload File: Upload a .pdb file from your local computer.
- Data Center: Select a .pdb file from the data center.
- External Database Import: Enter a PDB ID to download the corresponding file from the PDB database.
Protein Preprocessing
Determine whether to perform protein preprocessing based on the type of protein you upload. If the uploaded protein has already been preprocessed, you can directly click the next step. If not, it is recommended to enable the switch to perform preprocessing operations.
- Select Protein Chains to Keep: By default, all chain information in the uploaded .pdb file is displayed, and all chains are checked by default. When a chain is unchecked, the content in the protein visualization area will not show that chain.
- Remove Water Molecules/Ligands: By default, all small molecules in the pdb file and water molecules within 5Å of them are displayed. The system will automatically delete water molecules beyond 5Å, while water molecules within 5Å are left for users to decide whether to delete. Water molecules with water bridge effects are specially marked, and you can use the [Quick Delete Water Molecules Without Water Bridge Effects] button to remove water molecules without water bridge effects in one step.
- Protein Optimization Options Add missing residues and repair incorrect structures: Optional, checked by default; Add hydrogen atoms: Optional, checked by default; Adjust protonation states: Optional, checked by default with pH of 7.4; Optimize hydrogen bond network: Optional, checked by default; Energy minimization: Optional, checked by default with AMBER ff14SB force field selected;
AMBER ff14SB (recommended): ff14SB is a protein force field parameter set in the AMBER package used to describe atomic interactions in biomolecules. It is a force field parameter set in the AMBER14 package particularly suitable for protein systems, including additional parameters describing interactions between amino acid side chains and important residues in protein folding. AMBER ff14SB has high accuracy and reliability in describing protein conformation and dynamic properties.
AMBER ff15IPQ: ff15ipq is an improved protein force field parameter set in the AMBER14 package with higher accuracy and reliability compared to AMBER ff14ipq. AMBER ff15ipq includes more polarization effects and hydrogen bond parameters, enabling more accurate description of protein electronic structure.
AMBER96: AMBER96 is an early version of the AMBER package. After years of development and optimization, newer versions such as AMBER14 and AMBER18 are now available. However, AMBER96 is still widely used in biomolecular simulation, especially for early research and some classic case simulations.
AMBER99SB: AMBER99sb is an improved version of the AMBER99 force field, including additional parameters describing interactions between amino acid side chains and important residues in protein folding. AMBER has high accuracy and reliability in describing protein conformation and dynamic properties.
CHARMM36: CHARMM36 has high accuracy and reliability in describing protein conformation and dynamic properties. It is widely used in research on proteins and protein-ligand interactions, and is one of the commonly used force field parameter sets in the biomolecular simulation field.
(2) Peptide Input
- Upload File: Upload files in .fasta, .fas, .fa, or .txt format from your local computer.
- Data Center: Import fasta from the data center.
- Text Input: Directly enter peptide sequence text in the format: >sequence_name\nsequence_content, supports multiple sequences. Peptide input supports 20 standard amino acids and 72 non-standard amino acids, as shown below: • 20 standard amino acids: G, A, V, L, I, P, F, Y, W, S, T, C, M, N, Q, D, E, K, R, H • 72 non-standard amino acids, using [XXX] format, e.g.: RMF[HYP]R[PTR]NAPYL HYP, SEP, TYS, ALY, TPO, PTR, DAL, MLE, M3L, DLE, DLY, AIB, MSE, DPR, MVA, NLE, MLY, SAR, ABA, FME, DAR, ORN, CGU, DPN, DTY, DTR, 4BF, DGL, DCY, MK8, MP8, GHP, ALC, BMT, MLZ, DVA, 3FG, DAS, 7ID, DSN, AR7, MEA, PHI, MAA, LPD, KCR, PCA, DGN, 2MR, DHI, ASA, MLU, YCP, DSG, DTH, OMY, FP9, DPP, HCS, SET, DBB, BTK, DAM, IIL, 3MY, SLL, PFF, HRG, DIL, DNE, MED, D0C
(3) Set Docking Parameters
Docking Method
Select the docking method. Currently, there is only one docking method available: RAPiDock.
Docking Center & Coordinate Settings
Two methods are supported for defining the docking center: selecting a peptide ligand in the complex and customizing the docking site. The coordinates displayed by default are randomly assigned by the system, with length, width, and height set to default values. These parameters represent the position and size of the binding pocket.
- Select a peptide ligand in the complex as the docking site. This option is only applicable when the complex contains a peptide ligand. When there are multiple peptide ligands in the complex, the system displays the one with the largest molecular mass by default, and users can switch to other peptide ligands in the dropdown box. The system calculates the geometric center (XYZ coordinates) based on the size of the peptide ligand and sets an appropriate box size.
- Customize the docking site. In custom mode, users can place the mouse directly in the 3D display area. After clicking on a residue, the corresponding coordinate information of that residue will be displayed on the parameter panel, and the system also provides a default length, width, and height. However, the specific size of the pocket needs to be set by users based on their understanding of the protein pocket. A pocket that is too small will lead to inaccurate calculation results, while a pocket that is too large will increase calculation time.
Number of Conformations
Set the maximum number of conformations to output for each peptide ligand after docking.
Task Name
Can be customized or use the default task name assigned by the system.
3. Result Analysis
The calculation result page is shown in Figure 1. Upper left
- Task ID: Displays the ID of this task in the backend.
- Workspace: The workspace this task belongs to.
- Valid Results: Number displayed in the current table / total number of outputs.
- Scoring Function: Ref2015. Ref2015 is the latest version of the Rosetta energy function, specifically designed to evaluate the binding energy of protein-protein and protein-peptide interactions. This scoring function comprehensively considers various physicochemical factors such as van der Waals forces, electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and desolvation effects. A lower score indicates more stable binding.
- Sequence Legend: The color of amino acid characters in the SEQUENCE column of the table below, divided into five categories: hydrophobic, polar, positively charged, negatively charged, and glycine.
- Self-Docking Assessment: When setting docking parameters, if the peptide ligand in the complex is selected as the center, self-docking will be performed on that ligand, and the self-docking assessment will be displayed and shown below (if multiple self-docking results are output in the table, the value in the self-docking assessment corresponds to the structure with the lowest REF2015 score).
Lower left
- ID: The output ID of the peptide, the first is the number of different peptide sequences, the second is the number of different poses of the same sequence.
- SEQUENCE: The sequence of the input peptide.
- REF2015: The scoring function. Click to rank by this column; clicking a third time restores the initial sorting.
- Advanced Filter: Filter the results in the table below based on the Ref2015 value.
- Favorites Only: Filter the favorited results in the table.
Upper right
- Parameters: Parameters related to this task.
- Save: Save results to the database.
- Download: Download results to local computer.
Lower right 3D visualization interface, which displays according to the checked status of the first column of the table on the left; you can also enter the ID from the table in the input box after "Current Peptide Chain" below and press Enter to display a specific molecule, or click the left and right symbols to browse different peptides.
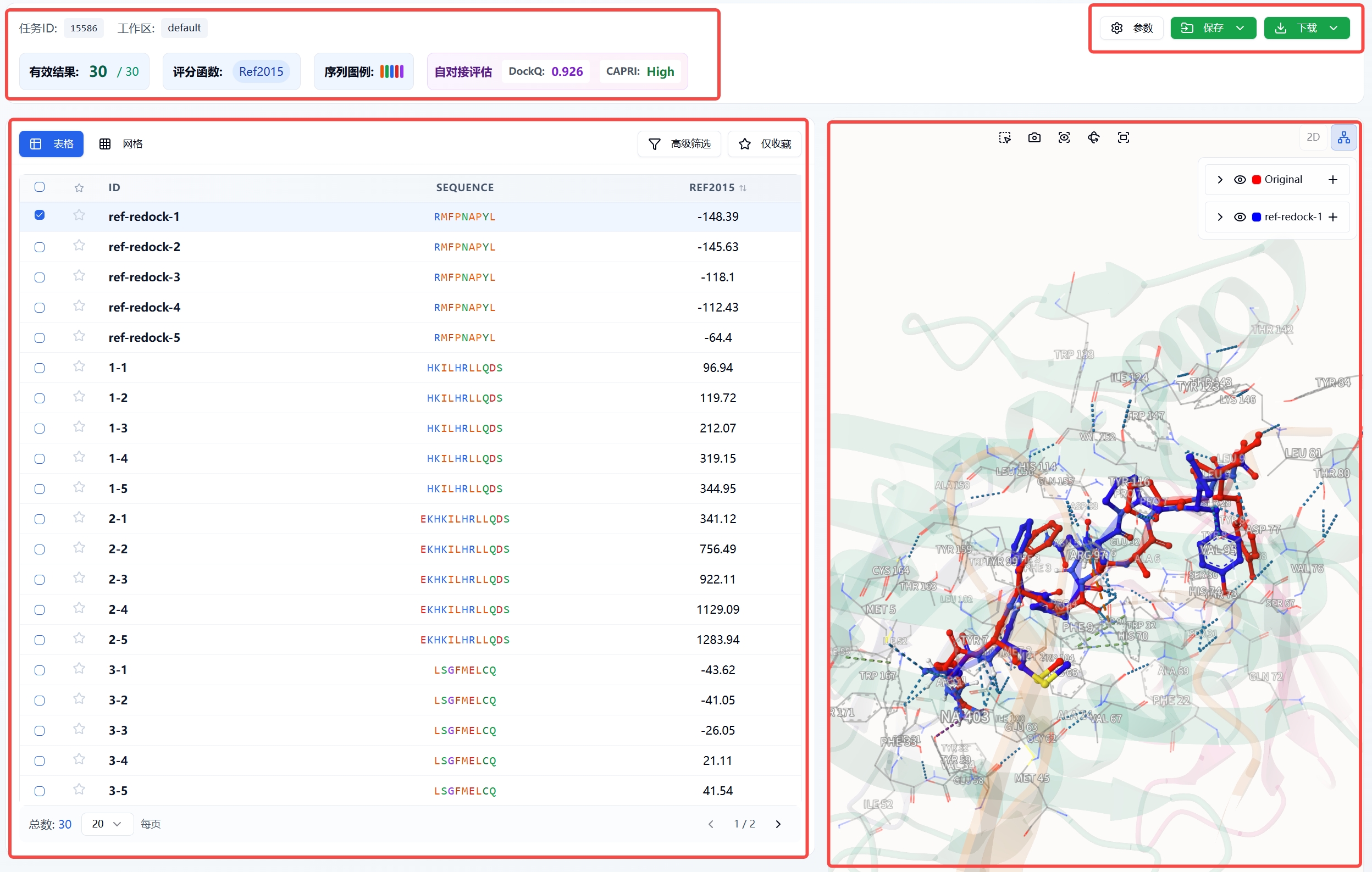
Figure 1. Calculation result page
